Strategic Plan Framework
In order to create a cogent plan for following that organization’s vision, a strategy framework covers a range of viewpoints that are connected.
These interconnected framework perspectives and points encapsulate the factors at play that any organization must take into account while defining its strategy.
An integrated strategic framework delivers the following benefits:
- Improves communication and fidelity of objectives,
- Helps organizations to adapt rapidly,
- Enables the rationalizations of initiatives,
- Supports capability-centric investment,
- Provides the ability to monitor an organization’s progress towards strategic objectives,
- Supports organization alignment.
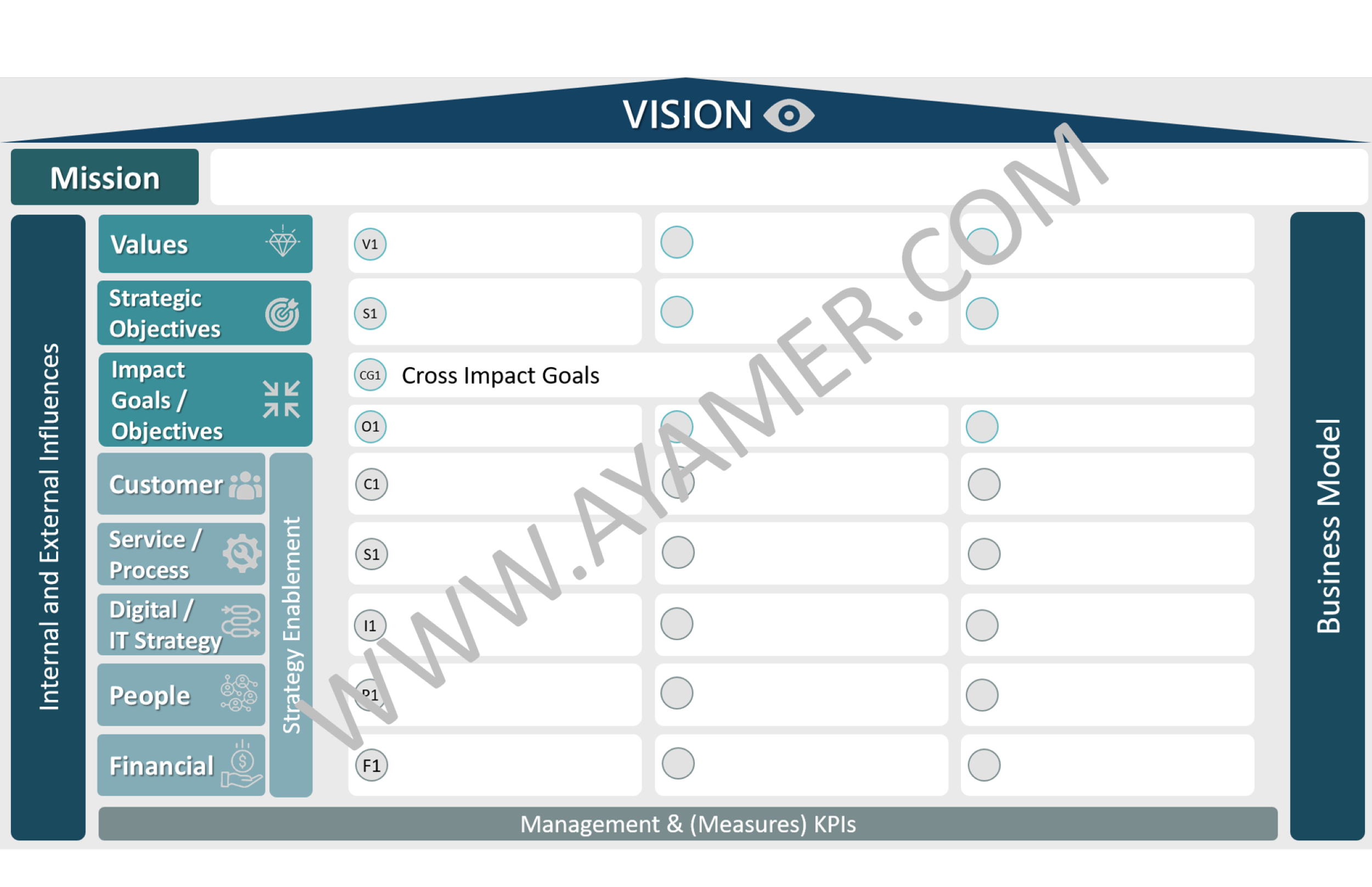
Strategic Plan Framework Contents:
· Vision:
An organization’s overarching strategy plan includes a live declaration called a vision statement. It is usually written when a business is just getting off the ground and aids in guiding the enterprise in the desired path.
A strong vision statement should inspire, excite, and motivate. It should be an integral part of the business culture and lay out the organization’s future for all stakeholders, including investors and employees. It ought to provide employees a motivation to come into work each day and keep up their hard work for the business.
· Mission:
Emphasizes the present. An Organization’s immediate objectives and the steps it is taking to accomplish them are the main topics of a mission statement.
The mission statement supports the vision and serves to communicate purpose and direction to employees, customers, vendors and other stakeholders.
· Values:
Outlines the fundamental values that serve as the organization’s and its culture’s compass.
A moral compass is created for the organization and its employees in a values-led workplace.
It establishes a benchmark against which actions can be judged and directs decision-making. These guiding principles are a shared framework that the leadership follows.
· Strategic Objectives:
Strategic objectives are declarations of purpose that aid in establishing an overall vision, as well as goals and actionable tasks, for an organization in order to assist it reach a desired result.
A strategic goal is most effective when it can be measured by statistics or other visible data.
Businesses establish strategic objectives to advance their corporate vision, harmonize their goals, and influence decisions that have an impact on daily productivity at all organizational levels.
· Impact Goals and Objectives:
Broad assertions about a department or a business unit. Objectives are the more specific, quantifiable measures we take to reach the goal.
Goals should be S.M.A.R.T
With the help of the S.M.A.R.T. approach, we can create a sound strategy with attainable objectives.
S à Specific: Writing goals should be as straightforward as feasible, focusing on a single aim.
Mà Measurable: Goals must be quantifiable so that concrete evidence may be provided along the way. This can be done by designating a deadline for the accomplishment.
A à Achievable: Goals should be designed like a good workout. They should stretch slightly, but not cause stress.
R à Relevant: Examine the goals. Make sure it’s relevant and realistic.
Tà Time-bound: Goals should be tied to a timetable that generates a realistic feeling of urgency, building a positive tension that will help to move forward.
· Strategy Enablement:
The Perpetual Strategy Enablement program is built on the fundamental tenet that most businesses already have the talent, technology, services, and processes needed to create successful strategies and implement them provide the motivation, facilitation, structures, and (occasionally) discipline to assist organizations in realizing goals through five dimensions:
o Customers: creating value for the consumers based on the product or service.
Set goals for outstanding customer service with actionable objectives to help achieve this outcome.
o Services / Process:
The strategic objectives for business processes and operations center on altering or restructuring how a business runs. An organization may decide to re-engineer and assess the way they produce a product or service with the aim of creating a more efficient process in order to efficiently set production targets. Other process and operational goals can include business-to-business or business-to-consumer strategies and methods.
o Digital / IT Strategy:
Establishing how digital and IT strategy merge in response to an organization’s growing reliance on technology by seeking new opportunities and maximize the use of current capabilities.
Identifying which technologies an organization will use and how it will contribute in achieving and support the strategic goals and objectives, how to utilize the technology envisioned in the digital strategy, how it will be used to perform business operations.
o People:
Organizations seek to develop staff knowledge and capacities with particular initiatives in order to create strategic learning objectives. In order to fulfill overall performance goals, a corporation can aim to invest in its people through strategic objectives for training.
o Financial:
Financial strategic objectives are developed to assist businesses in forecasting profits, creating budgets, and calculating organizational expenses. They enable a business to concentrate on the financial requirements of their enterprise with precise actions to raise or lower prices, review spending, examine revenue trends, and plan for financial expansion.
· Internal and External Influences:
It specifies an influencer area that details the types of influencers to which the organization is exposed.
Internal effects are those that a business can manage (Infrastructure, Policies, Assumptions,..) , whereas external influences are those that a business cannot manage (Customers, Partners, Vendors,..)
· Business Model:
A business model explains and describes how an organization operates and generates revenue. A strategic plan outlines and clarifies the why, where, and how a business model will be employed to achieve these objectives.
A business model shows how corporate resources are organized and grouped in a process to create value (benefit) for the client and profits for the business owner. The business model thus addresses the fundamental purpose of a company’s existence in general, which is achieved by paying a customer and an effective businessperson who has revenues that are greater than costs and who, as a result, makes a profit.
· Strategic Management and KPIs:
The constant planning, monitoring, analysis, and assessment of all requirements that an organization requires to accomplish its goals and objectives is known as strategic management. Organizations will have to reevaluate their success methods on a regular basis as a result of changes in the business environment. The strategic management process aids businesses in taking stock of their current condition, developing and implementing management plans, and evaluating their efficacy.
A Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a quantifiable metric that reflects how well an organization is achieving its stated goals and objectives.

